Neurodegenerative Disease Models
More Disease Modeling Services
Preselected Neurodegenerative Disease-Relevant Models
The ability to quickly install variant alleles in C. elegans and zebrafish, and quantitatively measure the variant phenotypes provides researchers a path to rapidly address the consequence of gene variation for answering questions of neurodegenerative disease biology, including neurological disorders and neurodegenerative disorders.
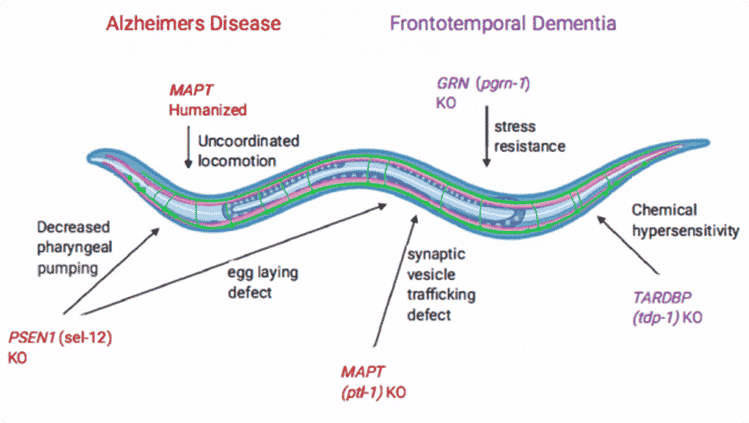
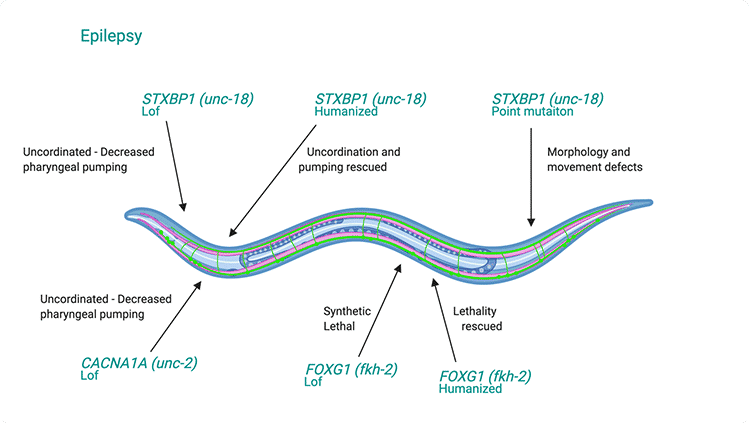
The images below illustrate C. elegans as a transgenic model for studying gene variations associated with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Frontotemporal Dementia (FD), and Epilepsy Disorder (ED), showcasing the superior cell survival and cell differentiation capabilities of these models.
C. elegans as a transgenic model for studying Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FD).
Testing new compounds and formulations to understand whether they are functionally effective on disease phenotypes is key in clinical trials for addressing cognitive impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction related to these neurodegenerative diseases.
- Red text: AD human genes expressed with worm gene homologue (in parentheses).
- Purple text: FD human gene expressed with worm gene homologue (in parentheses), highlighting the importance of understanding synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline through genetic manipulation.
- Phenotypes observed are written close to the arrow.
Featured Offerings
We have preselected disease-relevant models and validated their genetic identity with PCR and sequencing. These humanized model systems can serve as another efficient toolset to study human diseases, offering insights into cell engineering workflow and cell performance.

Models for Alzheimer’s Disease
Strains carrying genetic mutations that are associated with Alzheimer’s disease, validated via PCR and sequencing, are critical for understanding neurobiological aging and the development of effective therapeutic strategies, including the exploration of gene therapy programs.

Models for Epilepsy Disorder
Models carrying genetic mutations that are associated with Epilepsy disorder, validated via PCR and sequencing.
Other Offerings
We can create other neurodegenerative disease-relevant models using zebrafish and C. elegans, including Frontotemporal Degeneration and Huntington’s diseases, utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing tools for gene editing efficiency.
Neurodegenerative Disease Models FAQs
1. What are Neurodegenerative Disease Models?
Neurodegenerative disease models, including those using C. elegans and zebrafish, are vital research tools designed to study the underlying mechanisms of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases. By replicating genetic mutations and observing phenotypic outcomes, these models offer insights into neurodegenerative disorders, aiding in the development of therapeutic strategies and clinical trials aimed at mitigating cognitive impairment and neurofibrillary tangles commonly associated with these conditions.
2. How Do C. elegans Serve in Studying Alzheimer’s Disease Research?
C. elegans models play a crucial role in Alzheimer’s disease research by allowing scientists to study transgenic mice and dopaminergic neurons in a controlled environment. These models help in understanding the genetic basis of Alzheimer’s, particularly in the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and the impact on cognitive decline. This research is pivotal in exploring therapeutic strategies and advancing clinical trials for new treatments.
3. What Role Do Neurodegenerative Disease Models Play in Clinical Trials?
Models of neurodegenerative diseases are instrumental in clinical trials by providing a foundational understanding of diseases at the genetic and cellular level, including the study of mitochondrial dysfunction and blood-brain barrier permeability. These models facilitate the development and testing of new drugs and treatments, aiming to address cognitive impairment and slow disease progression, thus representing a cornerstone of clinical trials in neurology.
4: How Can Neurodegenerative Disease Models Help in Understanding Cognitive Decline?
Through the study of specific models, such as C. elegans and zebrafish, researchers can observe the effects of genetic mutations on neurological disorders, offering insights into the processes leading to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. This research is crucial for identifying potential therapeutic strategies to prevent or reduce cognitive impairment, leveraging findings to guide clinical trials and treatment development.
5. What Does the Future Hold for Therapeutic Strategies in Treating Neurodegenerative Disorders?
The future of therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative disorders looks promising, with ongoing research in 3D models, pluripotent stem cells, and embryonic stem cells offering new avenues for treatment. Innovations in genetic manipulation and the development of blood-brain barrier-penetrating drugs are among the exciting prospects. Additionally, clinical trials continue to evolve, incorporating findings from neurobiological aging studies to improve treatment outcomes for conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases.
Ready to get started?
Ready to connect with us to learn more about working with our company or our technology?
Submit your inquiry below & we will get back to you soon.