A client wanted a knockout (KO) of an embryonic lethal gene. We could not make this line using our standard methods. Instead, we inserted two loxP sites. One in the first intron of the gene and the second in the 3’utr. After we confirmed this line by PCR and sequencing, we injected this line with a ubiquitously expressing Cre Recombinase plasmid.
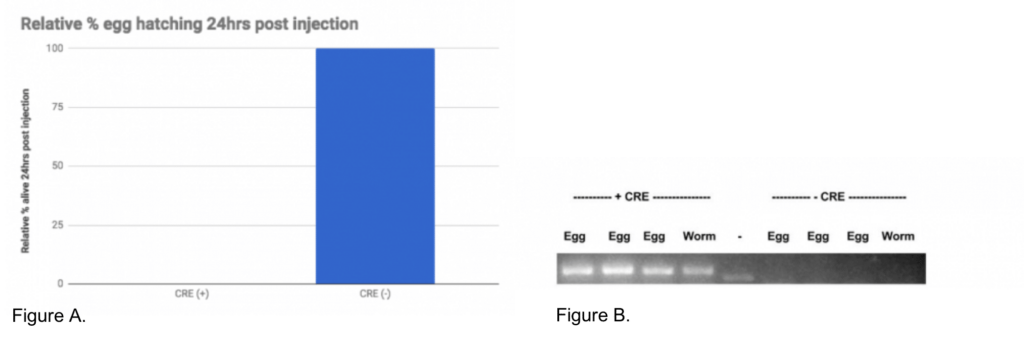
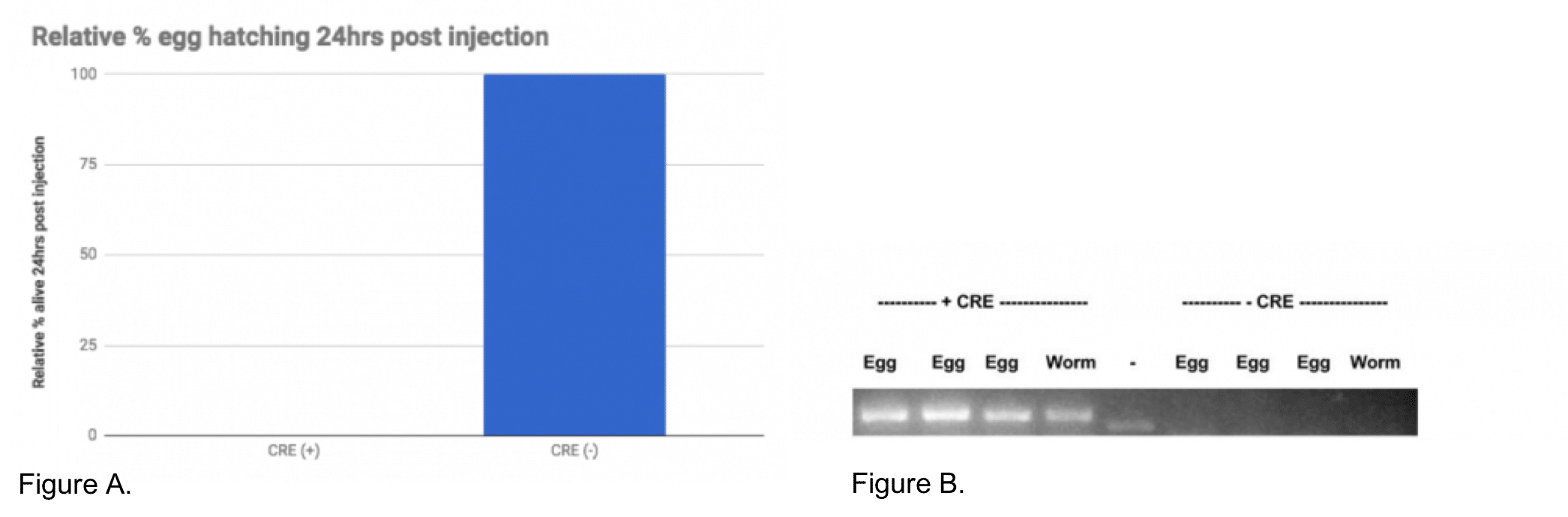
We found while the uninjected animals could reproduce, the Cre injected animals did not (Figure A). We tested recombination by PCR and found that only the Cre injected progeny showed recombination of the loxP sites (Figure B).
This line could be used to study KO of this gene in adulthood or in specific tissues, something that was not previously possible due to the embryonic lethality caused by the KO of this gene.