Professional CRO and Gene Editing Services
right model. right insight.
Our platforms help pharma, biotech, and academics ensure success by providing biologically relevant data to make critical decisions fast.
Breaking News:
InVivo Biosystems appoints Kat McCormick, Ph.D. as the new CEO.
Gene Editing and CRO Services
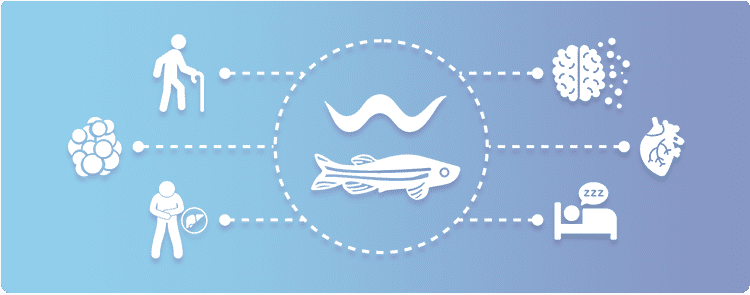
In Vivo Models
Preclinical CRO Services
Bridge the data gap between cell culture and rodent models. Rapidly conduct preclinical studies to de-risk your clinical trial.
Our Technologies
An expert in CRISPR genome editing for creating custom genome edited zebrafish and C. elegans, our CRISPR genome editing platform enables preclinical studies and drug discovery by providing insights you need to derisk your clinical trial or decide the next phase of product devleopment.
What's New with InViVO BioSystems

Sample Report
Download our sample data report to see an example of the dataset you would receive if you partnered with us.

White Paper
Our newest white paper focus on the gut microbiome and discusses the questions: What is the microbiome? How does it help or hinder health? And, what does recent research indicate?

Customer Story
Dr. Marius Galyan (CEO and Founder at Galyan Bio, Inc.) shares his experience in working with InVivo Biosystems and how the Longevity Platform delivered the results he needed to accelerate his research.
About InVivo Biosystems

2010
Year Established

45
Number of Employees

11
Number of PhDs

18
Average Years of Experience in Genetics

4000+
Number of Preclinical Models Created

247
Publications
READY TO GET STARTED?
Ready to connect with us to learn more about working with our company or our technology?
Submit your inquiry below & we will get back to you soon.